Sodium benzoate: The hidden dangers of a common food preservative
10/08/2025 / By Laura Harris

- Sodium benzoate is a synthetic preservative commonly used in acidic foods, beverages and medications to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life, but it has no nutritional value.
- It’s derived from benzoic acid and produced synthetically from toluene, raising concerns due to its petroleum-based origins and long-term health effects.
- Health risks include potential formation of benzene (a known carcinogen), disruption of gut health, oxidative stress and links to hyperactivity in children.
- Sodium benzoate is commonly found in sodas, fruit juices, salad dressings, pickles, processed snacks and certain pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Natural alternatives include rosemary extract, citric acid, fermentation and vitamin E – safer options that consumers can choose to reduce exposure.
In the modern food and pharmaceutical industries, preservatives play a crucial role in extending shelf life and preventing spoilage. However, not all preservatives are created equal. One controversial additive, sodium benzoate, has raised concerns among health-conscious consumers and researchers alike. Derived from benzoic acid, this synthetic preservative is widely used in beverages, processed foods and medications, but at what cost to your health?
Role of sodium benzoate in food preservation
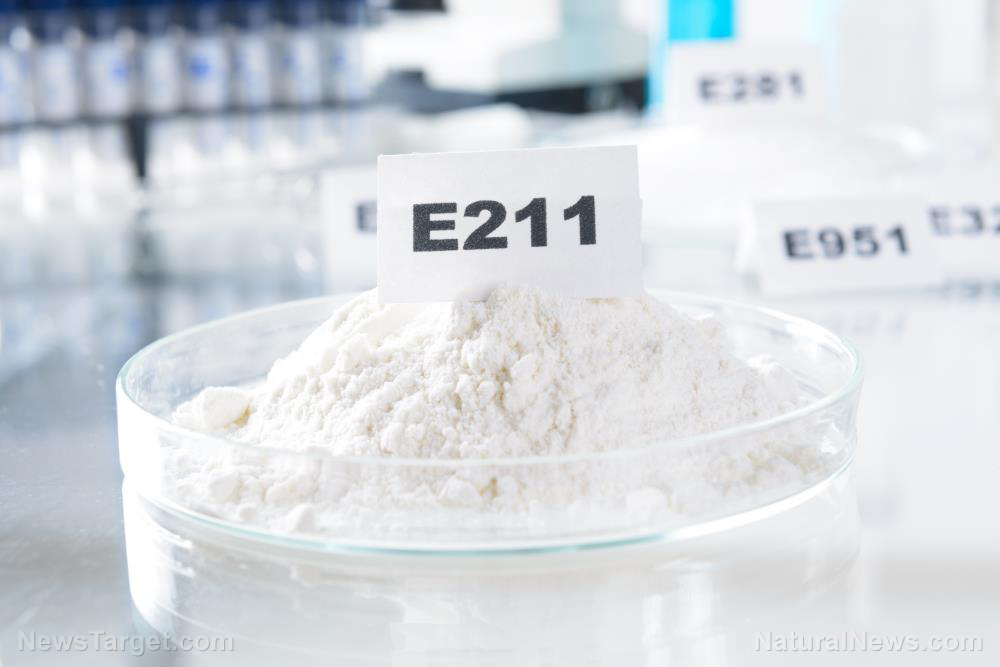
Sodium benzoate, also known as E211, is a synthetic compound that serves as the sodium salt of benzoic acid. Initially introduced in the 19th century, it gained widespread use as a preservative in the early 20th century due to its ability to inhibit the growth of fungi and bacteria in acidic environments.
Originally derived from benzoin resin, modern production now relies on synthetic methods using toluene, a petroleum byproduct, making it a cost-effective and widely available additive. In 1908, the U.S. FDA approved its use for food preservation, solidifying its role in the food and beverage industry. Beyond food, sodium benzoate is also utilized in antiseptics, pharmaceuticals, tobacco products, dyes and rust inhibitors. Though effective, its synthetic nature has sparked concerns about long-term health effects, prompting discussions around informed consumer choices and safer alternatives.
Unlike nutrient-rich superfoods or natural preservatives like rosemary extract or vitamin E, sodium benzoate serves no nutritional purpose – its sole function is preservation. It effectively extends shelf life by preventing spoilage in acidic foods and beverages (with a pH of 4.5 or lower).
Commonly found in sodas, fruit juices, pickles, salad dressings, condiments and processed snacks, sodium benzoate is also utilized in pharmaceuticals, including cough syrups, liquid medications and cosmetics. Due to its strong antimicrobial properties, manufacturers often prefer sodium benzoate over natural alternatives, despite increasing concerns about its potential health risks.
Health risks associated with sodium benzoate
While regulatory agencies like the FDA classify sodium benzoate as “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS) in small doses, emerging research highlights significant health concerns.
One major danger lies in its chemical interaction with ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and potassium benzoate, which can form benzene – a known carcinogen. The FDA has acknowledged that exposure to heat and light accelerates this reaction, raising concerns given benzene’s classification by the American Cancer Society as a cancer-causing agent. Beyond benzene formation, studies suggest sodium benzoate disrupts the gut microbiome, potentially harming immune function and digestion.
Additionally, research from the UK Food Standards Agency links it to increased hyperactivity and ADHD symptoms in children. A 2016 study also raised alarms about oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction caused by sodium benzoate, which may impair cellular energy production and even contribute to DNA damage. Despite its widespread use in sodas and processed foods, these risks underscore the need for caution, particularly with frequent consumption.
Common foods containing sodium benzoate
You may unknowingly consume sodium benzoate in:
- Carbonated soft drinks (soda)
- Commercial fruit juices
- Salad dressings and condiments
- Pickles and fermented foods
- Processed snack foods
Recipes and dishes where sodium benzoate lurks:
- Store-bought salsa
- Bottled lemon/lime juice
- Packaged pie fillings
- Pre-made smoothies & fruit punches
Natural alternatives to sodium benzoate
Instead of sodium benzoate, opt for foods preserved with:
- Rosemary extract (rich in antioxidants)
- Citric acid (derived from citrus fruits)
- Fermentation (probiotic-rich preservation)
- Vitamin E (tocopherols)
In short, sodium benzoate effectively preserves food, but its potential health risks outweigh its benefits. By choosing whole, unprocessed foods and researching product ingredients, you can minimize exposure to harmful additives.
This story is not medical advice and is not intended to treat or cure any disease. Always consult with a qualified naturopathic physician for personalized advice about your specific health situation or concern.
Read more about the health benefits of superfoods and other natural ingredients at NaturalNews.com, your trusted source for wellness insights and nutritional knowledge.
For cutting-edge tools to expand your understanding of natural health, try Brighteon.ai, an innovative AI model created by Mike Adams, the Health Ranger. This free, downloadable tool is designed to decentralize knowledge, bypass censorship, and empower individuals with actionable information.
If you’re passionate about nutrition, natural medicine, and uncensored discussions, visit Brighteon.com, a free speech video platform, and join our vibrant communities on Brighteon.IO and Brighteon.social. Dive into open conversations about food, ingredients and holistic health today!
Watch this video to learn more about sodium benzoate.
This video is from the Daily Videos channel on Brighteon.com.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
clean food watch, food additives, food science, food supply, grocery, health science, poison, preservatives, products, sodium benzoate, stop eating poison, toxic chemicals, toxic ingredients, toxins
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2019 Dangerous.News
All content posted on this site is protected under Free Speech. Dangerous.News is not responsible for content written by contributing authors. The information on this site is provided for educational and entertainment purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional advice of any kind. Dangerous.News assumes no responsibility for the use or misuse of this material. All trademarks, registered trademarks and service marks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.